PS: An Image is Worth 16x16 words: transformers for image recognition at scale
Paper link: AN IMAGE IS WORTH 16X16 WORDS: TRANSFORMERS FOR IMAGE RECOGNITION AT SCALE
What
Transforms have become the choice in natural language processing. In computer vision CNN still are the dominant, classic resnet like architetures still are the state of the art. Idea: is to apply a standard transformer directly to images. The image is splited in patches and provide the sequence of linear embeddings of these patches as input to a Transformer. ViT does not generalize well when trained on insufficient amounts of data.
Why
Transformers were proposed for machine learning translation, and have since becomestate of the art method in manu NLP tasks. Large transformer models are often pre-trained on large corpora and then fine tuned for the task at hand. Naive application of sel-attention to images would requre that each pixelattends to every other pixel, does not scale to realistic inputs. Many aproximations were tried, many demonstrate promising results, but complex engineering to be implemented efficiently. There is interest in combining CNN with forms with self-attention. Only one model (trained in a unserpervised fashion) that uses Transformers with global self-attention to full images, wich applies Transformers to images pixels after reducing image resolution and color space.
How
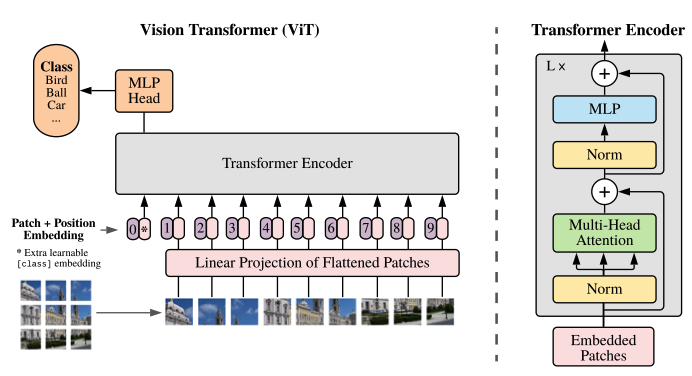
2D image is flattened. Similar to BERT [class] token x_class is a learnable embedding. The classification head is implemented by a MLP with one hidden layer at pre-training timeand by a single linear layer at fine-tuning. 1D learnable embeddings, since no performance gains from using 2D-aware position embeddings.
The transformer encoder consists of alternating layers of multiheaded self-attention. ViT was pre-trained on large datasets and fine-tune to smallerdownstream tasks. Remove the pre-trained prediction head and attach a zero-initialized feedorward layer. Is often beneficial to fine-tune at higher resolution than pre-training. When feeding higher resolution images, since the patch size is the same this means larger effective sequences.
Models: ResNet, ViT and Hybrid (CNN). Pre training on different datasets of varying size and evaluate manu benchmark tasks. ViT attains state of the art on most recognition benchmarks at lower pre training cost. Self supervision in ViT holds promise for the future.
Datasets: ImageNEt 1k classes and 1.3M images, ImageNet-21k 21k classesand 14M images, JFT 18K classes and 303M high-resolution images. Transfer models to ImageNEt Validation labels and the cleaned-up ReaL labels.
Model Variants: ViT based on BERT. “Base” and “Large” directly adopted from BERT, added new “Huge” model. Transformers sequence length is inversely proportional to the square of the patch size thus models with smaller patch size are computationally more expensive. Baseline CNN, was used ResNet with Group Normalization and Used standardized convolutions.
Results
ViT-L/16 pre-trained on JFT-300M outperforms BiT-L on all tasks while requiring lesscomputational resources to train. ViT-H/14 further improves the performance. ViT-/16 model pre-trained on the public ImageNet-21k dataset performs well on most datasets too, while taking fewer resources to pre-train (TPUv3 for 30 days.
Conclusion
First work with no Self-attention in computer vision. Instead the image is interpreted as a sequence of patches and process it by a standard transformer. Is Scalable and works really well when coupled with pre-training on large datasets. Matching and exceeding the state of the art on many images classification datasets, whilst being relatively cheap to pre-train.
Self-supervised pre-training methods need to be explored.